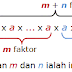
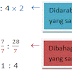
2010/06/23
NST
KUALA LUMPUR: A school-based assessment system may be used to replace an exam-oriented education system in the country, said Deputy Prime Minister Tan Sri Muhyiddin Yassin.
Muhyiddin, who is also Education Minister, said the Examination Board would determine the type of questions that can be used by teachers for such assessment in schools.
"We will replace exams with an assessment system. It has not been finalised but a study has been done and found to be acceptable because such a system is used in many countries.
"The system might not be very different from other countries, provided the education system - how teachers teach and how students study - is not affected. The concern is how to evaluate achievement of students - through examinations or assessment," he told the Dewan Rakyat when winding up debate on the 10th Malaysia Plan, for his ministry, here today.
He added that the government would not make hasty decisions on policy matters like proposals to scrap the Ujian Pencapaian Sekolah Rendah (UPSR) and Penilaian Menengah Rendah (PMR) exams.
"Many experts have said that it should have been done long ago, why now? We have carried out a research and study since 2007 because we have a team to look into such issues," he said.
Muhyiddin said reducing public examinations would actually save the government money in aspects of management, human resource and the burden of teachers to carry out such examinations process.
As for revamping technical, vocational and skills education system to become part of the premier education system of the country, Muhyiddin said the government would increase the number of vocational schools and introduce new curriculums to cater for growing demands.
"I myself am going to chair the meeting at ministry level to look at the main changes involved in the revamp of vocational, curriculum, infrastructure, facilities and training," he said.
He added that the Education Ministry would also take over the implementation of the Permata Negara programme from 2012.
The Permata programme, a model for the national childcare and early childhood education curriculum, is an effort by the government to educate children below the age of five and the system had been expanded to 457 centres nationwide, benefiting 17,565 children so far.
Meanwhile, Muhyiddin said overall RM26.093 billion was allocated to the Education Ministry as a whole, to carry out 15,324 projects, including an additional 808 projects under the Economic Stimulus Package.
"Until June 15, 8,870 project have been successfully completed, 5,312 projects are in various stages of implementation and 942 will be carried forward to 10MP," he said.
Muhyiddin said as of May 31, 2010 the ministry had spent RM16.668 billion or 85.12 per cent of the overall allocation. -- BERNAMA
NST
KUALA LUMPUR: A school-based assessment system may be used to replace an exam-oriented education system in the country, said Deputy Prime Minister Tan Sri Muhyiddin Yassin.
Muhyiddin, who is also Education Minister, said the Examination Board would determine the type of questions that can be used by teachers for such assessment in schools.
"We will replace exams with an assessment system. It has not been finalised but a study has been done and found to be acceptable because such a system is used in many countries.
"The system might not be very different from other countries, provided the education system - how teachers teach and how students study - is not affected. The concern is how to evaluate achievement of students - through examinations or assessment," he told the Dewan Rakyat when winding up debate on the 10th Malaysia Plan, for his ministry, here today.
He added that the government would not make hasty decisions on policy matters like proposals to scrap the Ujian Pencapaian Sekolah Rendah (UPSR) and Penilaian Menengah Rendah (PMR) exams.
"Many experts have said that it should have been done long ago, why now? We have carried out a research and study since 2007 because we have a team to look into such issues," he said.
Muhyiddin said reducing public examinations would actually save the government money in aspects of management, human resource and the burden of teachers to carry out such examinations process.
As for revamping technical, vocational and skills education system to become part of the premier education system of the country, Muhyiddin said the government would increase the number of vocational schools and introduce new curriculums to cater for growing demands.
"I myself am going to chair the meeting at ministry level to look at the main changes involved in the revamp of vocational, curriculum, infrastructure, facilities and training," he said.
He added that the Education Ministry would also take over the implementation of the Permata Negara programme from 2012.
The Permata programme, a model for the national childcare and early childhood education curriculum, is an effort by the government to educate children below the age of five and the system had been expanded to 457 centres nationwide, benefiting 17,565 children so far.
Meanwhile, Muhyiddin said overall RM26.093 billion was allocated to the Education Ministry as a whole, to carry out 15,324 projects, including an additional 808 projects under the Economic Stimulus Package.
"Until June 15, 8,870 project have been successfully completed, 5,312 projects are in various stages of implementation and 942 will be carried forward to 10MP," he said.
Muhyiddin said as of May 31, 2010 the ministry had spent RM16.668 billion or 85.12 per cent of the overall allocation. -- BERNAMA